How to Shiny
Zach Spiegel
What is Shiny? (Recap)
An R package that allows for more functionality within the software
Allows users to create interactive web pages for data science

How to Install Shiny
Since Shiny is not in base R, you will need to install it…
- Install package:
- Load package:
The installing packages step only needs to be done once!
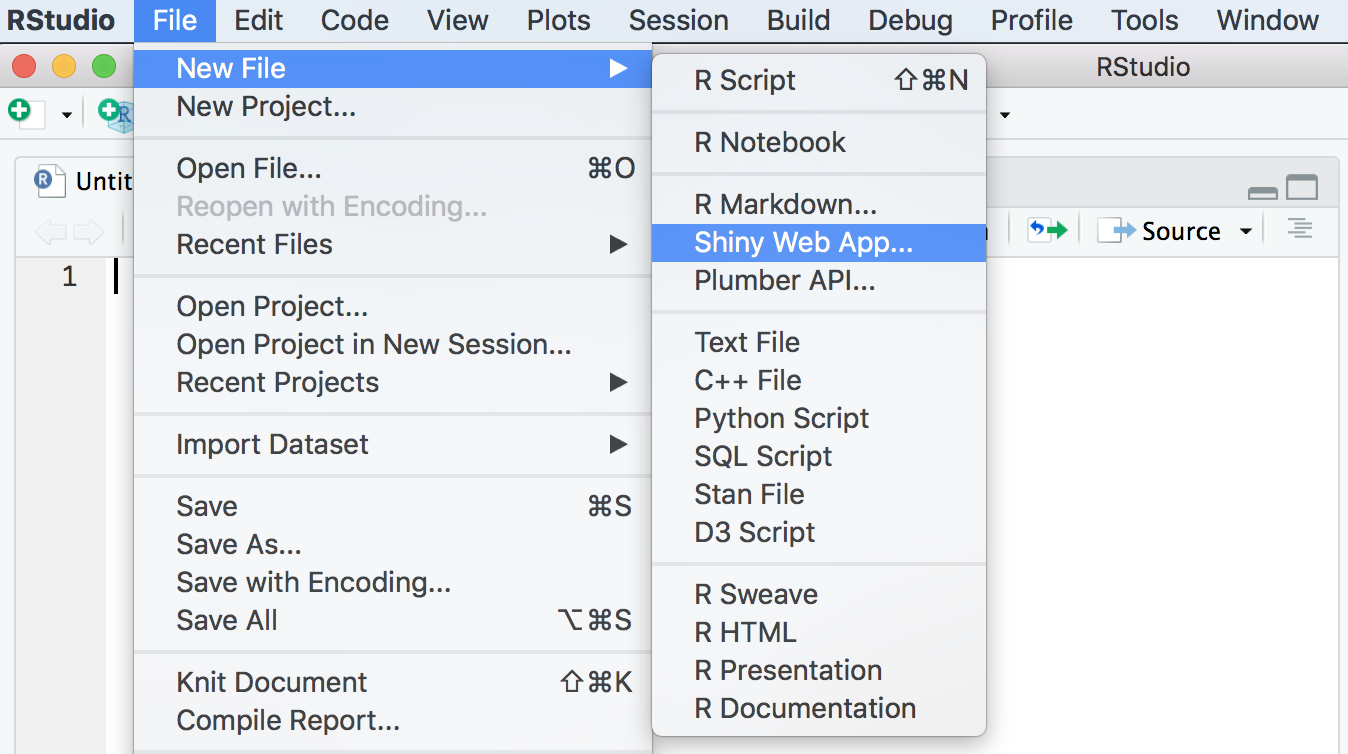
Getting Started
File > New File > Shiny Web App
Application type: Single File is best (easier to keep track of code)
Example of a Shiny App
Iris k-means clustering
Sidebar and Plot (UI)
ui <- pageWithSidebar(
headerPanel('Iris k-means clustering'), ## Title
sidebarPanel( ## Creates a panel on the left side of screen
selectInput('xcol', 'X Variable', vars),
## Dropdown for picking X variable
selectInput('ycol', 'Y Variable', vars, selected = vars[[2]]),
## Dropdown for picking Y variable
numericInput('clusters', 'Cluster count', 3, min = 1, max = 9)
## Option to pick number of clusters
),
mainPanel(
plotOutput('plot1') ## Names your output variable
)
)Remember, we need to do our server-side code or this will not work!
Actual Shiny app may differ when viewed outside of Quarto
Back-end Code (Server)
server <- function(input, output, session) {
## Combine the selected variables into a new data frame
selectedData <- reactive({
iris[, c(input$xcol, input$ycol)]
## selectedData is reactive!
## Contains only selected X and Y variables
})
clusters <- reactive({
kmeans(selectedData(), input$clusters)
})
## Performs clustering based on number of user selected clustersBack-end Code (Server)
output$plot1 <- renderPlot({
palette(c("#E41A1C", "#377EB8", "#4DAF4A", "#984EA3",
"#FF7F00", "#FFFF33", "#A65628", "#F781BF", "#999999"))
## Renders the plot using custom colors
par(mar = c(5.1, 4.1, 0, 1))
plot(selectedData(),
col = clusters()$cluster,
pch = 20, cex = 3)
points(clusters()$centers, pch = 4, cex = 4, lwd = 4)
})
## Plots points
## You will use ggplot instead of this syntax!
}Run the App!
Since you will be using a combined file, you must run this command to run the app.
Creating your App
- Load your Packages (I used a lot - don’t need all to begin!)
## Important packages
library(ggplot2)
library(shiny)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(ggplotlyExtra) ## Convert ggplot2 plots to plotly
library(plotly)
library(bslib) ## Extra functionality within Shiny
library(shinyWidgets) ## Extra functionality within Shiny
library(gghalves)
library(ggforce)
library(ggdist)
library(shinycssloaders) ## Adds loading wheel to outputs
library(shinytitle) ## Gives your page a name on browserCreating your App cont.
- Load and Clean Data
data <- read.csv("health_status_data.csv")
## Load csv as "data" variable
data <- data %>% select(-SAMPLE1, -SAMPLE2, -SAMPLE3, -SAMPLE4, -SAMPLE5,-RI_1, -RI_2, -RI_3, -RI_4, -RI_5, -RI_6, -RI_7, -RI_8)
## Selecting all columns EXCEPT the ones above
data <- data %>% mutate( ## this is a pipe (%>%)
SEX = case_when(SEX == 0 ~ "Male",
SEX == 1 ~ "Female",
SEX == 2 ~ "Intersex",
SEX == 3 ~ "Other")
)
## data <- data means making our changes PERMANENTKeep variable names concise and easily recognizable!
Creating your App cont.
- Create UI and Server Code
Using Plotly for graphs is often better because of its extra functionality.
Creating your App cont.
- Create UI and Server Code
Same with DT for datatables.
Links to Other Resources